Antibodies and Immunity – how do they relate to one another?
Antibodies play a central role in the complex tapestry of our immune system, acting as defenders against invading pathogens. But how exactly do antibodies and immunity intertwine, and what role does each play in keeping us healthy? We delve into this fascinating relationship to unlock the secrets of our body's defense mechanisms. Get antibodies from Biochain, the custom antibody suppliers in india.
Understanding Antibodies:
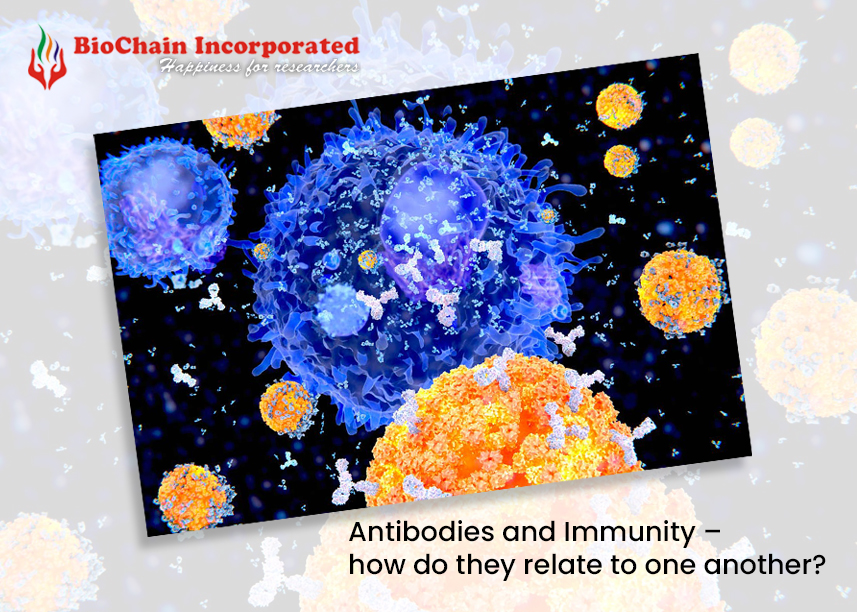
Antibodies, also known as immunoglobulins, are Y-shaped proteins produced by special white blood cells called B cells. These proteins are adapted to recognize and neutralize specific antigens, which are molecules on the surface of pathogens such as viruses, bacteria or parasites.
When our body is exposed to a foreign invader, such as a virus, B cells kick in. They go through a process called somatic hypermutation and class switching, where they fine-tune their antibodies to better target and neutralize the threat. Once antibodies are produced, they circulate in the bloodstream ready to bind to any corresponding antigens they encounter.
The Role of Antibodies in Immunity:
Antibodies are key players in both innate and adaptive immunity. In innate immunity, they act as the first line of defense, preventing pathogens from entering cells and marking them for destruction by other immune cells. This process helps contain the infection until an adaptive immune response is triggered.
In adaptive immunity, antibodies play a central role in the humoral immune response. They work with other immune cells, such as T cells, to target specific pathogens. Antibodies can neutralize viruses by preventing them from entering cells, agglutinate bacteria to facilitate their destruction by phagocytes, and activate the complement system to enhance immune responses. Receive the high quality antibodies from Biochain, one of the best custom antibody suppliers in india.
Dynamic relationship:
The relationship between antibodies and immunity is dynamic and multifaceted. Although antibodies are essential for recognizing and neutralizing pathogens, immunity encompasses a broader set of mechanisms designed to protect the body against infectious diseases.Immunity can be innate or acquired, active or passive, and cellular or humoral. Innate immunity provides an immediate, nonspecific defense mechanism against many pathogens, while acquired immunity develops over time in response to specific antigens and can provide long-term protection.
Antibodies play a key role in acquired immunity, where they play a key role in creating immunological memory. After initial exposure to a pathogen, memory B cells are formed that can rapidly produce large amounts of antibodies upon re-exposure to the same antigen. This process is the basis of vaccination, in which the immune system is prepared to respond quickly and effectively to future infections.
Conclusion:
In short, antibodies and immunity are closely related to our body's defense system. Antibodies act as molecular soldiers that recognize and neutralize pathogens, while immunity encompasses a broader set of mechanisms designed to protect the body against infectious diseases.Understanding the interaction between antibodies and immunity is essential to developing strategies to fight infectious diseases, from vaccination to immunotherapy. By harnessing the power of our immune system and the specificity of our antibodies, we can open up new ways to prevent and treat many diseases, ultimately promoting the health and well-being of all. Contact Biochain, the best antibody suppliers in india. Contact Now.


.png)

.png)


.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)